You can perform different types of certificate replacement depending on your company policy and requirements for the system that you are configuring. You can perform certificate replacement from the vSphere Client, by using the vSphere Certificate Manager utility, or manually by using the CLIs included with your installation.
The VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA) is included in each vCenter Server deployment. VMCA provisions each node, each vCenter Server solution user, and each ESXi host with a certificate that is signed by VMCA as the certificate authority.
You can replace the default certificates. For vCenter Server components, you can use a set of command-line tools included in your installation. You have several options.
Replacing Certificates with VMCA-Signed Certificates
If your VMCA certificate expires or you want to replace it for other reasons, you can use the certificate management CLIs to perform that process. By default, the VMCA root certificate expires after 10 years, and all certificates that VMCA signs expire when the root certificate expires, that is, after a maximum of 10 years.
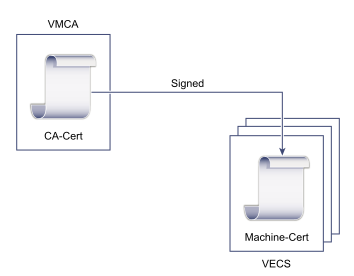
- Replace Machine SSL Certificate with VMCA Certificate
- Replace Solution User Certificate with VMCA Certificate
For manual certificate replacement, see Replace Existing VMCA-Signed Certificates with New VMCA-Signed Certificates Using the CLI.
Making VMCA an Intermediate Certificate Authority
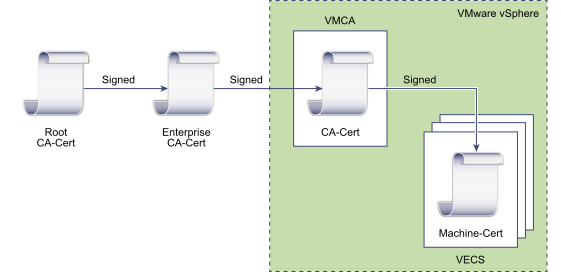
- Replace VMCA Root Certificate with Custom Signing Certificate and Replace All Certificates
- Replace Machine SSL Certificate with VMCA Certificate (multi-node enhanced linked mode deployment)
- Replace Solution User Certificate with VMCA Certificate (multi-node enhanced linked mode deployment)
For manual certificate replacement, see Make VMCA Into an Intermediate Certificate Authority Using the CLI.
Replacing VMCA-Signed Certificates with Custom Certificates
You can replace the existing VMCA-signed certificates with custom certificates. If you use that approach, you are responsible for all certificate provisioning and monitoring.
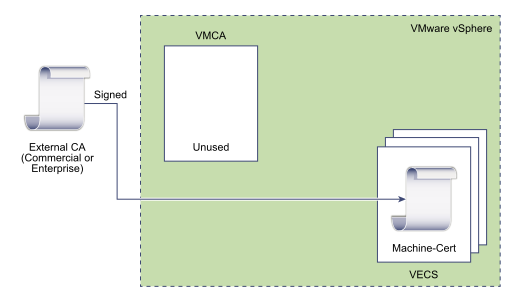
- Replace Machine SSL Certificate with Custom Certificate
- Replace Solution User Certificates with Custom Certificates
For manual certificate replacement, see Replace Certificates with Custom Certificates Using the CLI.
You can also use the vSphere Client to generate a CSR for a machine SSL certificate (custom), and replace the certificate after the CA returns it. See Generate Certificate Signing Request for Machine SSL Certificate Using the vSphere Client (Custom Certificates).
Using the Hybrid Approach to Certificate Deployment
In the hybrid approach, you can have VMCA supply some of the certificates, but use custom certificates for other parts of your infrastructure. For example, because solution user certificates are used only to authenticate to vCenter Single Sign-On, consider having VMCA provision those certificates. Replace the machine SSL certificates with custom certificates to secure all SSL traffic.
Company policy often does not allow intermediate CAs. For those cases, hybrid deployment is a good solution. It minimizes the number of certificates to replace, and secures all traffic. The hybrid deployment leaves only internal traffic, that is, solution user traffic, to use the default VMCA-signed certificates.
For more information, see the blog post titled New Product Walkthrough - Hybrid vSphere SSL Certificate Replacement at http://vmware.com/go/hybridvmca.
ESXi Certificate Replacement
For ESXi hosts, you can change certificate provisioning behavior from the vSphere Client. See the vSphere Security documentation for details.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| VMware Certificate Authority mode (default) | When you renew certificates from the vSphere Client, VMCA issues the certificates for the hosts. If you changed the VMCA root certificate to include a certificate chain, the host certificates include the full chain. |
| Custom Certificate Authority mode | Allows you to update and use certificates manually that are not signed or issued by VMCA. |
| Thumbprint mode | Can be used to retain 5.5 certificates during refresh. Use this mode only temporarily in debugging situations. |