Learn how to configure vSphere HA for a Supervisor running on a vSAN stretched cluster so that to provide HA for workloads.
Prerequisites
- Enable and configure a vSAN stretched cluster.
- Activate a Supervisor on the vSphere cluster configured as a vSAN stretched cluster.
Procedure
- Locate the vSphere cluster where the Supervisor is deployed respectively on a vSAN stretched cluster.
- Select Configure and select vSphere Availability.
- Next to vSphere HA Turned On, click Edit.
- Configure Failure and Responses settings.
Option Value Description Host monitoring Turned on Uses network heartbeat to determine the status of hosts participating in the cluster, and whether a corrective action is required, such as restarting a VM on a different host from the cluster Response for Host Isolation Power off restart VMs Determines what happens to the VMs on an isolated host, that is a host that cannot communicate to other hosts in the cluster nor reach the isolation response IP address. You configure this setting to Power off and restart, because a clean shutdown is not possible on an isolated host, and the access to the vSAN Datastore and the ability to write to disks is lost. - Configure Admission Control.
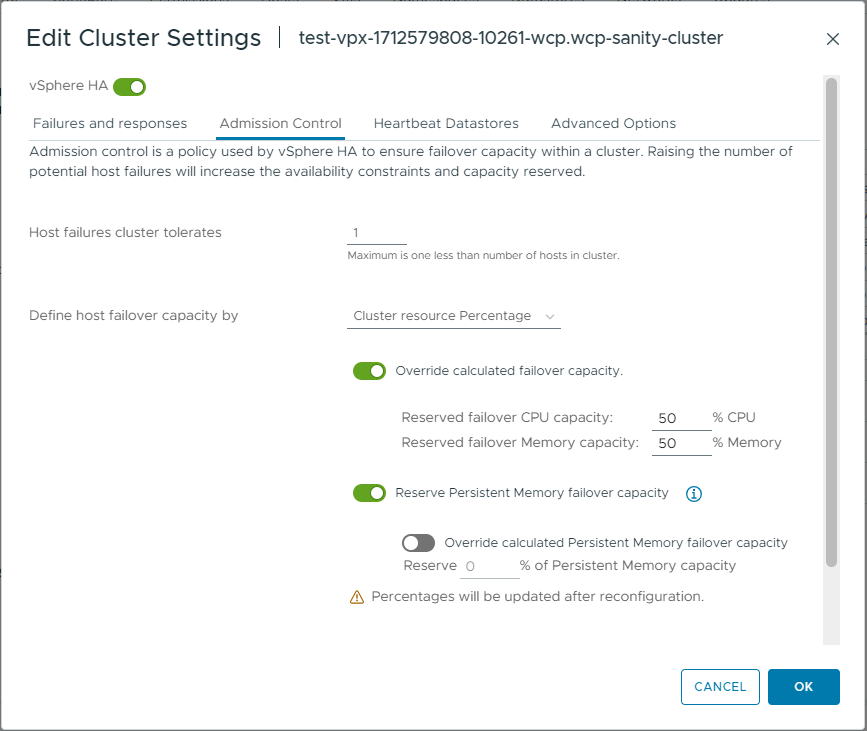
The compute capacity in a vSAN stretched cluster is typically equally divided between the two sites in the cluster. You need to ensure that all the VMs on site 1 can be restarted on site 2 when an entire site goes down. To achieve this, you reserve 50% of the cluster's capacity for failover to allow restart of all the VMs during site failure.
- Set Define host failover capacity by to Cluster resource Percentage.
- Enable Override calculated failover capacity and set the CPU and memory reservations to 50% each.
With this setting, vSphere HA ensures that 50% of cluster's aggregate CPU and memory resources are reserved for failover.
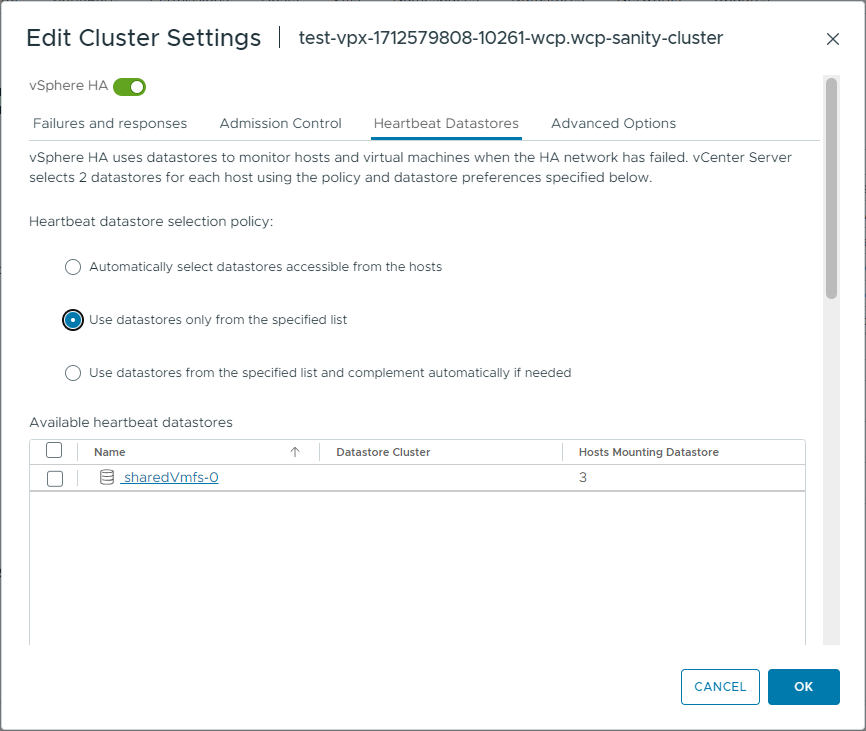
- Configure Datastore Heartbeating.
In addition to network heartbeating, vSphere HA provides datastore hearbeating for determining the state of the hosts in the cluster. However, a vSAN datastore cannot be used for heartbeating and you must deactivate this function for the vSAN datastore.Note: If any additional datastore (other than vSAN) is available and if it is accessible by an alternate network path, independent of the vSAN network, then using heartbeat datastores is fully supported.To not use datastore heartbeating for the vSAN datastore, select Use datastores only from the specified list and make sure that the vSAN datastore is not selected. You will still see an alert that there are less than the required heartbeat datastores, you can disable that alarm by configuring das.ignoreInsufficientHbDatastore = true.
- Configure isolation response addresses.
When vSphere HA is enabled on a vSAN cluster, HA uses network heartbeat to validate the state of an ESXi host.
In a vSAN environment, vSphere HA uses the vSAN traffic network for communication. This is different from traditional vSphere environments where vSphere HA uses the management network for communication. However, even in a vSAN environment, vSphere HA continues using the default gateway of the management network for isolation detection responses. For this reason, you must configure isolation response IP addresses that reside on the vSAN network to allow HA to react to a vSAN network failure and trigger host isolation response.
It is recommended that you specify two additional isolation response addresses, and each of these addresses should be site-specific - one isolation address residing in site 1 and the other residing in site 2. This enables vSphere HA to validate host isolation even in the case of network failure between sites. Use the following settings for additional isolation response addresses:- das.isolationaddress0. Set the value to an IP address on the vSAN network which resides on site 1.
- das.isolationaddress1. Set the value to an IP address on the vSAN network that resides on the site 2.
- das.usedefaultisolationaddress. Set to false.
- Save the settings.
- Configure HA restart priority for individual VMs.
In case of host or site failure, a possibility exists that the resources are insufficient to restart all the VMs in the vSAN cluster. Therefore, you have to ensure that certain VMs that are of high importance, such as the Supervisor control plane VMs, are restarted first. To do so, configure vSphere HA restart priority to individual VMs, as follows:
- Highest - Supervisor control plan VMs, NSX Edge VMs, and NSX Advanced Load Balancer Service engine VMs.
- High - all TKG cluster control plane VMs.
- Medium - all TKG cluster worker VMs.
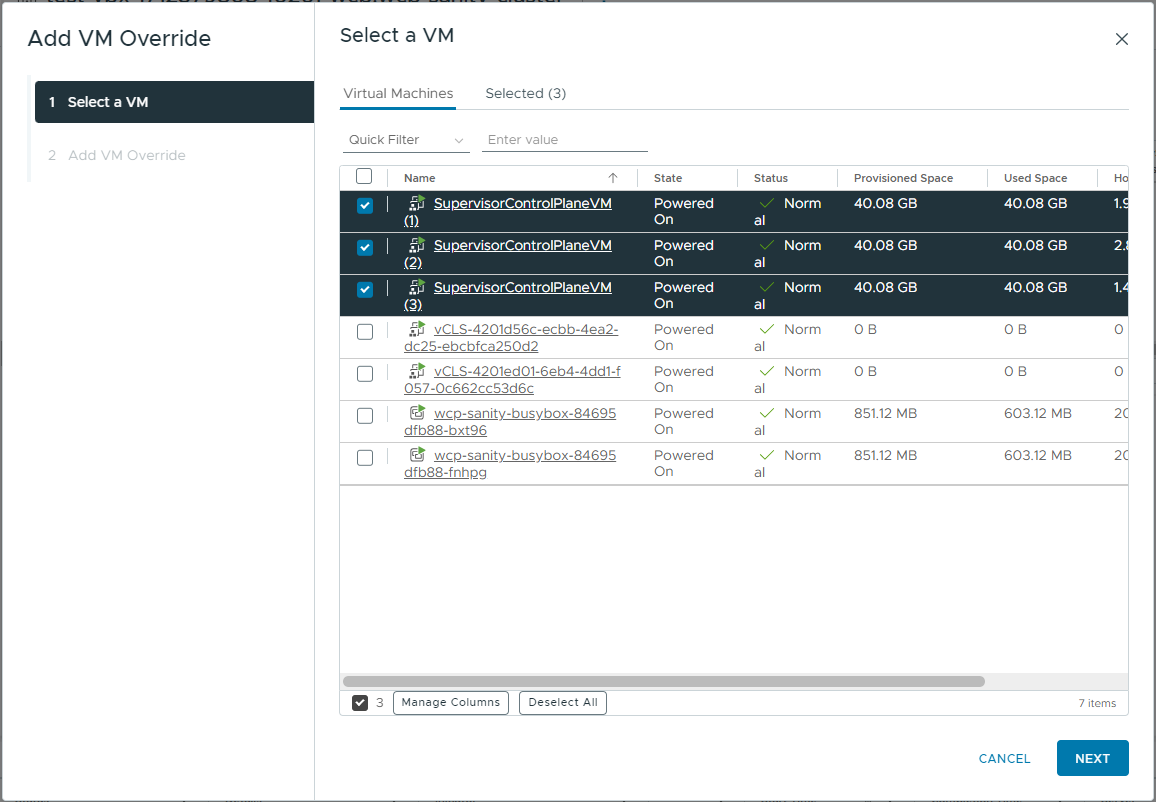
- On the cluster where the Supervisor is enabled, go to Configure > VM Overrides.
- Select VMs from the list, for example all the Supervisor control plane VMs, and click Next.
- Under vSphere HA, next to VM Restart Priority, select Override, and select a priority level, for example Highest.
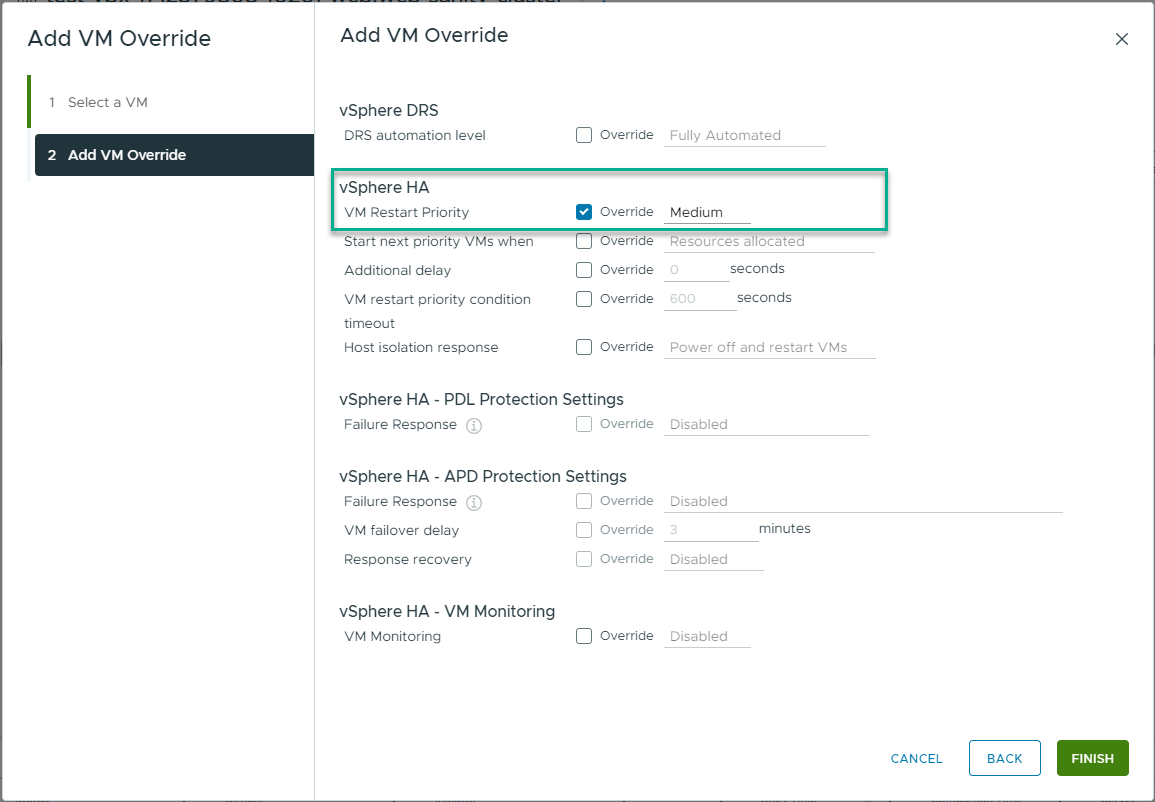
- Repeat the steps until you set restart priority to all the VMs described from above.
What to do next
Configure vSphere DRS VM and host groups and rule to affine Supervisor control plane VMs, and TKG cluster control plane and worker nodes.