Configure Identity Management
This topic explains how to enable and configure identity management in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (TKG) with a standalone management cluster.
About Enabling and Configuring Identity Management
You can enable identity management during or after management cluster deployment, by configuring an LDAPS or OIDC identity provider. Any workload clusters that you create after enabling identity management are automatically configured to use the same identity provider as the management cluster. To retroactively configure existing workload clusters with newly-enabled identity management, follow Enable Identity Management on Workload Clusters.
Enabling and configuring identity management includes the following steps. If you want to use standard, non-admin kubeconfig files for access to management and workload clusters, after completing the steps in this topic, you must also configure role-based access control (RBAC) by following the instructions in Configure RBAC.
(Recommended) Enabling and configuring identity management during management cluster deployment:
- Obtain your identity provider details.
- Use the obtained details to configure LDAPS or OIDC in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
- After the management cluster has been created, confirm that the authentication service is running correctly and complete its configuration.
For instructions, see (Recommended) Enable and Configure Identity Management During Management Cluster Deployment below.
Enabling and configuring identity management after management cluster deployment:
- Obtain your identity provider details.
- Generate the Pinniped add-on secret for the management cluster.
- Confirm that the authentication service is running correctly and complete its configuration.
- If the management cluster manages any workload clusters, generate the Pinniped add-on secret for each workload cluster that was created before you enabled identity management.
For instructions, see Enable and Configure Identity Management in an Existing Deployment below.
(Recommended) Enable and Configure Identity Management During Management Cluster Deployment
This section explains how to enable and configure identity management during management cluster deployment.
Obtain Your Identity Provider Details
Before you can enable identity management, you must have an identity provider. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid supports LDAPS and OIDC identity providers.
- To use your company’s internal LDAPS server as the identity provider, obtain LDAPS information from your LDAP administrator.
- To use OIDC as the identity provider, you must have an account with an identity provider that supports the OpenID Connect standard, for example, Okta.
Example: Register a Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Application in Okta
To use Okta as your OIDC provider, you must create an account with Okta and register an application for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid with your account:
- If you do not have one, create an Okta account.
- Go to the Admin portal by clicking the Admin button.
- Go to Applications and click Create App Integration.
- For Sign-in method, select OIDC - OpenID Connect and for Application type, select Web Application, and then click Next.
- Give your application a name.
- Under Grant Type, under Client acting on behalf of a user, make sure that both Authorization Code and Refresh Token are selected.
- Enter a placeholder Sign-in redirect URI. For example, enter
http://localhost:8080/authorization-code/callback. You will update this with the real URL after you deploy the management cluster. - Under Assignments, assign people and groups to the application. The people and groups that you assign to the application will be the users who can access the management cluster and the workload clusters that you use it to deploy.
- Click Save.
- In the General tab for your application, copy and save the Client ID and Client secret. You will need these credentials when you deploy the management cluster.
ImportantAll OIDC providers must be configured to issue Refresh Tokens in order to use TKG 2.3 or greater.
Configure LDAPS or OIDC Settings in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
Use the obtained above details to configure LDAPS or OIDC in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid:
- If you are deploying your management cluster using the installer interface, configure LDAPS or OIDC in the Identity Management section. For instructions, see Configure Identity Management in Deploy Management Clusters with the Installer Interface.
-
If you are deploying your management cluster from a configuration file, set the
LDAP_*orOIDC_*variables in the configuration file.For example:
LDAP:
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: ldap LDAP_BIND_DN: "cn=bind-user,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com" LDAP_BIND_PASSWORD: "example-password" LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_BASE_DN: dc=example,dc=com LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_FILTER: &(objectClass=posixGroup)(memberUid={}) LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: cn LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_USER_ATTRIBUTE: uid LDAP_HOST: ldaps.example.com:636 LDAP_ROOT_CA_DATA_B64: "" LDAP_USER_SEARCH_BASE_DN: ou=people,dc=example,dc=com LDAP_USER_SEARCH_FILTER: &(objectClass=posixAccount)(uid={}) LDAP_USER_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: uidOIDC:
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: oidc OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_ID: 0oa2i[...]NKst4x7 OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_SECRET: 331!b70[...]60c_a10-72b4 OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_GROUPS_CLAIM: groups OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_ISSUER_URL: https://dev-[...].okta.com OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_SCOPES: openid,groups,email,offline_access OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_USERNAME_CLAIM: emailFor instructions on how to prepare a management cluster configuration file, see Create a Management Cluster Configuration File.
Complete the Configuration of Identity Management
After the management cluster has been deployed, finish configuring identity management by following these procedures, described in the sections below:
- Connect
kubectlto the management cluster. - Confirm that the authentication service is running correctly by checking its status, as described in Check the Status of the Identity Management Service.
- (OIDC Only) Provide the Callback URI to the OIDC Provider.
- To support using standard, non-admin
kubeconfigfiles to access the management cluster, Configure RBAC for a Management Cluster.
Connect kubectl to the Management Cluster
To configure identity management, you must obtain and use the admin context of the management cluster:
-
Get the
admincontext of the management cluster. The procedures in this topic use a management cluster namedid-mgmt-test.tanzu mc kubeconfig get id-mgmt-test --adminIf your management cluster is named
id-mgmt-test, you should see the confirmationCredentials of workload cluster 'id-mgmt-test' have been saved. You can now access the cluster by running 'kubectl config use-context id-mgmt-test-admin@id-mgmt-test'. Theadmincontext of a cluster gives you full access to the cluster without requiring authentication with your IDP. -
Set
kubectlto theadmincontext of the management cluster:kubectl config use-context id-mgmt-test-admin@id-mgmt-test
Check the Status of the Identity Management Service
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid uses Pinniped to integrate clusters with OIDC and LDAP identity providers. When you enable identity management, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid creates the pinniped-supervisor service in the pinniped-supervisor namespace and pinniped-concierge in the pinniped-concierge namespace. Follow the steps below to check the status of the Pinniped service and note the EXTERNAL-IP address at which the service is exposed.
-
Get information about the services that are running in the management cluster. The identity management service runs in the
pinniped-supervisornamespace:kubectl get services -n pinniped-supervisorYou see the following entry in the output:
vSphere with NSX Advanced Load Balancer (ALB):
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/pinniped-supervisor LoadBalancer 100.70.70.12 20.52.230.18 5556:31234/TCP 84mAmazon Web Services (AWS):
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/pinniped-supervisor LoadBalancer 100.69.13.66 ab1[...]71.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com 443:30865/TCP 56mAzure:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/pinniped-supervisor LoadBalancer 100.69.169.220 20.54.226.44 443:30451/TCP 84mvSphere without NSX ALB:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/pinniped-supervisor NodePort 100.70.70.12 <none> 5556:31234/TCP 84m -
Note the following information:
- vSphere with NSX ALB, AWS, and Azure: Note the external address of the
pinniped-supervisorservice, as listed underEXTERNAL-IP. - vSphere without NSX ALB: Note the port on which the
pinniped-supervisorservice is running. In the example above, this port is31234.
- vSphere with NSX ALB, AWS, and Azure: Note the external address of the
-
Check that all services in the management cluster are running.
kubectl get pods -AIt can take several minutes for the Pinniped service to be up and running. For example, on AWS and Azure deployments the service must wait for the
LoadBalancerIP addresses to be ready. Wait until you see thatpinniped-post-deploy-jobis completed before you proceed to the next steps.NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE [...] pinniped-supervisor pinniped-post-deploy-job-hq8fc 0/1 Completed 0 85m
NoteYou are able to run
kubectl get podsbecause you are using theadmincontext for the management cluster. Users who attempt to connect to the management cluster with the regular context will not be able to access its resources because they are not yet authorized to do so.
Check the Status of an LDAP Identity Management Service
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid uses Pinniped to integrate clusters with an LDAP identity service to expose the service endpoint. When you enable LDAP, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid creates the pinniped-supervisor service in the pinniped-supervisor namespace and the pinniped-concierge service in the pinniped-concierge namespace.
-
Check that all services in the management cluster are running:
kubectl get services -AIt can take several minutes for the Pinniped service to be up and running. For example, on AWS and Azure deployments the service must wait for the
LoadBalancerIP addresses to be ready. Wait until you see thatpinniped-post-deploy-jobis completed before you proceed to the next steps.NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE [...] pinniped-supervisor pinniped-post-deploy-job-hq8fc 0/1 Completed 0 85mNote
You are able to run
kubectl get podsbecause you are using theadmincontext for the management cluster. Users who attempt to connect to the management cluster with the regular context will not be able to access its resources because they are not yet authorized to do so. - Proceed to Configure RBAC for the Management Cluster.
(OIDC Only) Provide the Callback URI to the OIDC Provider
If you configured the management cluster to use OIDC authentication, you must provide the callback URI for that management cluster to your OIDC identity provider. For example, if you are using OIDC and your IDP is Okta, perform the following steps:
- Log in to your Okta account.
- In the main menu, go to Applications.
- Select the application that you created for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid.
- In the General Settings panel, click Edit.
-
Under Login, update Login redirect URIs to include the address of the node in which the
pinniped-supervisoris running:-
vSphere with NSX ALB, AWS, and Azure: Add the external IP address and port number of the
pinniped-supervisorservice that you noted in the previous procedure:https://EXTERNAL-IP/callback -
vSphere without NSX ALB: Add the IP address that you set as the API endpoint and the
pinniped-supervisorport number that you noted in the previous procedure:https://API-ENDPOINT-IP:31234/callbackIn all cases, you must specify
https, nothttp.
-
- Click Save.
Configure RBAC for the Management Cluster
If you plan to use standard, non-admin kubeconfig files for access to the management cluster, after completing the configuration of identity management, configure RBAC by following the instructions in Configure RBAC for a Management Cluster.
Enable and Configure Identity Management in an Existing Deployment
This section explains how to enable and configure identity management in an existing deployment.
Obtain Your Identity Provider Details
Follow the instructions in Obtain Your Identity Provider Details above.
Generate the Pinniped Add-on Secret for the Management Cluster
This procedure configures the Pinniped add-on and deploys the authentication components in your management cluster. To generate a Kubernetes secret for the Pinniped add-on:
-
Set the context of
kubectlto your management cluster. For example, with a management cluster namedid-mgmt-test:kubectl config use-context id-mgmt-test-admin@id-mgmt-test -
Create a cluster configuration file by copying the configuration settings that you defined when you deployed your management cluster into a new file. Add the following settings to the management cluster configuration file, including the OIDC or LDAP identity provider details:
Note
You need to set these variables only for management clusters.
# Identity management type. This must be "oidc" or "ldap". IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: # Explicitly set the namespace, which for management clusters is "tkg-system". NAMESPACE: tkg-system # Set these variables if you want to configure OIDC. OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_ID: OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_CLIENT_SECRET: OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_GROUPS_CLAIM: OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_ISSUER_URL: OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_SCOPES: "email,profile,groups,offline_access" OIDC_IDENTITY_PROVIDER_USERNAME_CLAIM: # Set these variables if you want to configure LDAP. LDAP_BIND_DN: LDAP_BIND_PASSWORD: LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_BASE_DN: LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_FILTER: LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: dn LDAP_GROUP_SEARCH_USER_ATTRIBUTE: dn LDAP_HOST: LDAP_ROOT_CA_DATA_B64: LDAP_USER_SEARCH_BASE_DN: LDAP_USER_SEARCH_FILTER: LDAP_USER_SEARCH_ID_ATTRIBUTE: dn LDAP_USER_SEARCH_NAME_ATTRIBUTE: # Set these variables if you want to configure certificate duration CERT_DURATION: 2160h CERT_RENEW_BEFORE: 360hTo see which of these variables are optional and can be omitted, go to Variables for Configuring Identity Providers - OIDC and Variables for Configuring Identity Providers - LDAP.
If your management cluster is behind a proxy, make sure the new configuration file includes your proxy configuration details:
TKG_HTTP_PROXY: TKG_HTTPS_PROXY: TKG_NO_PROXY:For more information about these variables, see Proxy Configuration.
vSphere: Change the
VSPHERE_CONTROL_PLANE_ENDPOINTconfiguration setting to an unused IP address, as a dummy value to pass internal checks. -
Make sure your local environment has
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPEset to eitheroidcorldap, and notnone:echo $IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPEIf this variable is set to
none, run anexportcommand to re-set it tooidcorldap. -
Set the
FILTER_BY_ADDON_TYPEenvironment variable toauthentication/pinnipedso thattanzu management-cluster createoperates only on Pinniped-related objects:export FILTER_BY_ADDON_TYPE="authentication/pinniped" -
Generate a secret for the Pinniped add-on:
tanzu management-cluster create CLUSTER-NAME --dry-run -f CLUSTER-CONFIG-FILE > CLUSTER-NAME-example-secret.yamlWhere:
CLUSTER-NAMEis the name of your target management cluster.CLUSTER-CONFIG-FILEis the configuration file that you created above.
The environment variable settings cause
tanzu management-cluster create --dry-runto generate a Kubernetes secret, not a full cluster manifest. -
Review the secret and then apply it to the management cluster. For example:
kubectl apply -f CLUSTER-NAME-example-secret.yaml -
After applying the secret, check the status of the Pinniped add-on by running the
kubectl get appcommand:$ kubectl get app CLUSTER-NAME-pinniped -n tkg-system NAME DESCRIPTION SINCE-DEPLOY AGE pinniped Reconcile succeeded 3m23s 7h50mIf the returned status is
Reconcile failed, run the following command to get details on the failure:kubectl get app CLUSTER-NAME-pinniped -n tkg-system -o yaml
Complete the Configuration of Identity Management
Follow the instructions in Complete the Configuration of Identity Management above.
Enable Identity Management on Workload Clusters
Any workload clusters that you create when you enable identity management in the management cluster are automatically configured to use the same identity management service.
Authenticate Users on a Machine Without a Browser
If your bootstrap machine is a jumpbox or other machine with no display, you can authenticate to a cluster from a browser running on your local machine. How you do this depends on the cluster’s Pinniped version, which comes from the Tanzu Kubernetes release that the cluster is based on:
| Cluster TKr version | Browserless authentication procedure |
|---|---|
| TKr v1.23.10 (default for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid v1.6.1) or later | Follow the instructions below |
| Clusters based on older TKrs or created by older versions of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid | Follow the Authenticate Users on a Machine Without a Browser procedure in the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid v1.4 documentation |
NoteTanzu Kubernetes Grid v2.4 does not support browserless CLI login based on non-interactive accounts or password grants.
-
From a terminal window on your local machine, run
sshto remotely log in to your bootstrap machine. -
Set the
TANZU_CLI_PINNIPED_AUTH_LOGIN_SKIP_BROWSER=trueenvironment variable. This adds the--skip-browseroption to thekubeconfigfor the cluster.# Linux export TANZU_CLI_PINNIPED_AUTH_LOGIN_SKIP_BROWSER=true # Windows set TANZU_CLI_PINNIPED_AUTH_LOGIN_SKIP_BROWSER=true -
Export the standard
kubeconfigfor the cluster to a local file. Note that the command does not include the--adminoption, so thekubeconfigthat is exported is the standardkubeconfig, not theadminversion. For example, to export thekubeconfigfile to/tmp/my-cluster-kubeconfig:-
For a management cluster, run:
tanzu mc kubeconfig get --export-file /tmp/my-cluster-kubeconfigYou should see confirmation that
You can now access the cluster by specifying '--kubeconfig /tmp/my-mgmt-cluster-kubeconfig' flag when using 'kubectl' command. -
For a workload cluster, run:
tanzu cluster kubeconfig get my-cluster --export-file /tmp/my-cluster-kubeconfig
-
-
Connect to the cluster by using the newly-created
kubeconfigfile:kubectl get pods -A --kubeconfig /tmp/my-cluster-kubeconfigThe CLI outputs a login link for your identity provider. For example:
Log in by visiting this link: https://10.180.105.166:31234/oauth2/authorize?access_type=offline&client_id=pinniped-cli&code_challenge=-aJ617vJZXZeEnHPab1V2_VHPmc5VwspFig5QQKyTwg&code_challenge_method=S256&nonce=cafaf8f4d2cb714ef8fb3320c1b088ba&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2F127.0.0.1%3A33087%2Fcallback&response_mode=form_post&response_type=code&scope=offline_access+openid+pinniped%3Arequest-audience&state=fff3d4d46b36359d5ba2f24fad471dd8 Optionally, paste your authorization code: -
Copy the link and paste it into a browser on your local machine.
-
In the browser, log in to your identity provider. A page appears prompting you to paste an authorization code into the CLI:
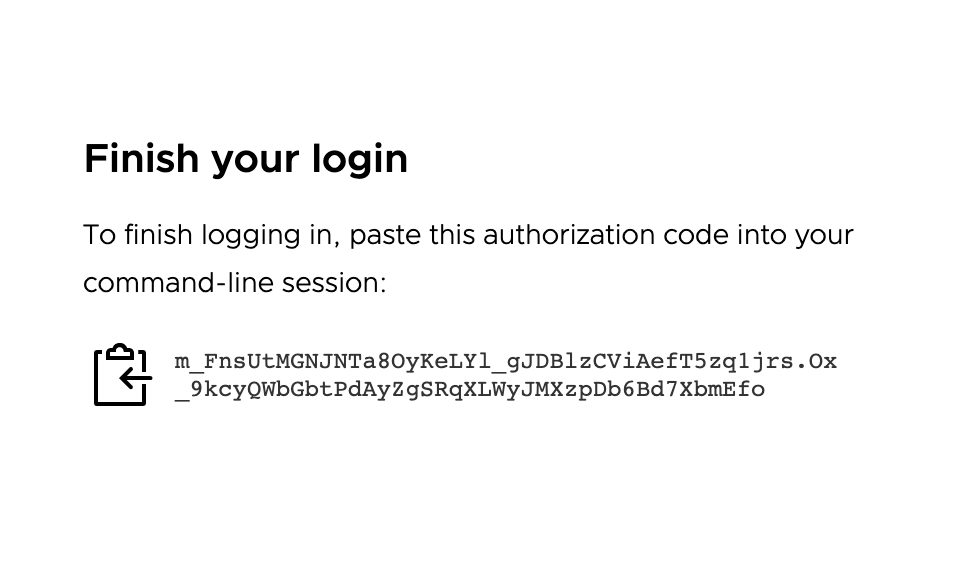
-
Copy the authorization code and paste it into the CLI, after the
Optionally, paste your authorization code:prompt. -
Connect to the cluster again by using the same
kubeconfigfile as you used previously:kubectl get pods -A --kubeconfig FILE-PATH-
If you already configured a role binding on the cluster for the authenticated user, the output shows the pod information.
-
If you have not configured a role binding on the cluster, you will see a message denying the user account access to the pods:
Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "user@example.com" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" at the cluster scope. This happens because the user has been successfully authenticated, but they are not yet authorized to access any resources on the cluster. To authorize the user to access the cluster resources, you must configure RBAC on the cluster by creating a cluster role binding:
-
Deactivate Identity Management in an Existing Deployment
To deactivate identity management in an existing deployment in which identity management is enabled:
-
Set the context of
kubectlto your management cluster. For example, with a management cluster namedid-mgmt-test:kubectl config use-context id-mgmt-test-admin@id-mgmt-test -
Retrieve the management cluster configuration file and edit it to set
IDENTITY_MANAGEMENT_TYPE: none. -
Generate a Pinniped Secret definition by running
tanzu management-cluster createwith--dry-runand filtering for Pinniped-related objects.FILTER_BY_ADDON_TYPE=authentication/pinniped tanzu management-cluster create --dry-run CLUSTER-CONFIG > PINNIPED-SECRETWhere
CLUSTER-CONFIGis the cluster configuration file andPINNIPED-SECRETis what you name the generated PinnipedSecretdefinition, such asmc-no-idp.yaml. -
Apply the new secret to deactivate Pinniped on the management cluster:
kubectl apply -f PINNIPED-SECRET -
After you deactivate Pinniped on the management cluster, its class-based clusters automatically deactivate, but you need to deactivate its legacy clusters manually:
-
List any Pinniped secrets remaining in the management cluster context:
kubectl get secret -A | grep pinniped-addon -
Investigate the secrets in the
kubectl get secretoutput, if any, using the secret name and namespace listed:kubectl get secret SECRET-NAME -n SECRET-NAMESPACE -o yaml -
Delete secrets that contain either:
type: tkg.tanzu.vmware.com/addon- these are legacy cluster secrets- any OIDC or LDAP configurations
kubectl delete secret SECRET-NAMEWhere
SECRET-NAMEis the value ofmetadata.nameset in theSecretspec.
-
What to Do Next
If you intend to use standard, non-admin kubeconfig files to give users access to your management and workload clusters, you must configure RBAC authorization:
- To configure RBAC for the management cluster, follow the instructions in Configure RBAC for a Management Cluster.
- After completing the steps in this topic, you can start creating workload clusters. To configure RBAC for the workload clusters, follow the instructions in Configure RBAC for a Workload Cluster.